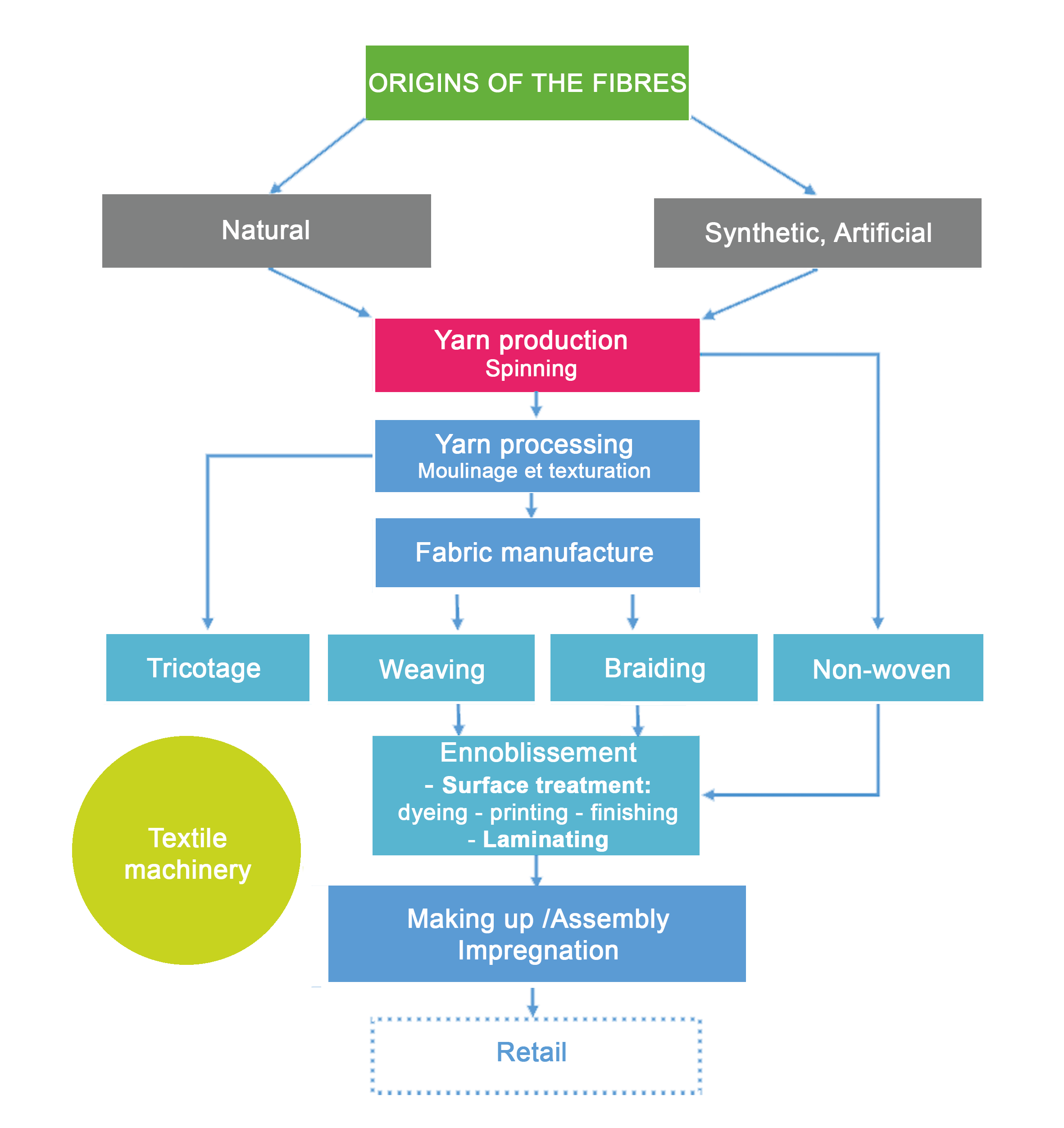
Glossary
- Fibres naturelles (végétales, minérales, animales) : obtenues par la transformation d’une matière première naturelle dont laine, coton, soie, lin, chanvre, jute, kapok, kenaf, coco, sisal
- Natural fibres (vegetable, mineral, animal): wool, cotton, silk, linen, hemp, jute, kapok, kenaf, coconut, sisal, …
- Artificial fibres: obtained by transformation of a natural raw material by chemical process (viscose – Modal and Tencel using cellulose from various plants, Lanital from milk casein, etc).
- Synthetic fibres: often derived from hydrocarbons or starch (polyester, polyamide, elastane, carbon, glass, aramid, poly lactic acid (PLA), polyurethane, polyethylene, polypropylene, etc).
- Non-woven: surface obtained by interlacing fibres via mechanical processes (needles, air jet, water jet), chemical or thermal. Mainly used in low-cost technical textiles (wipes, hygiene products, single-use products in the medical sector, structural supports in aeronautics, in the automotive industry, etc).
- Downtwisting / Texturing: used to twist together several fibres and filaments to modify the technical characteristics and provide functionalities (elasticity, swelling, resistance, etc).
- Knitting: the art of looping one or more threads to form intertwined stitches in a well-defined sequence. This technique gives a naturally stretchy fabric. There is also 3D knitting.
- Weaving: production process by interweaving warp yarns and weft yarns. The threads constituting the length of the fabric are called warp threads and the threads constituting the width of the fabric are the weft threads. There is also 3D weaving.
- Braiding: used in ropes and trimmings, braids are obtained by the oblique interlacing of several threads (unlike ribbon, which is made by weaving parallel threads).
- Finishing: term designating the different stages that will modify the surface appearance of fabrics: bleaching, dyeing, printing, mechanical or chemical finishes, coating. Certain treatments can be carried out on the yarn, on the fabrics and even on the finished products.